DO YOU KNOW WHAT CAUSES UTI?
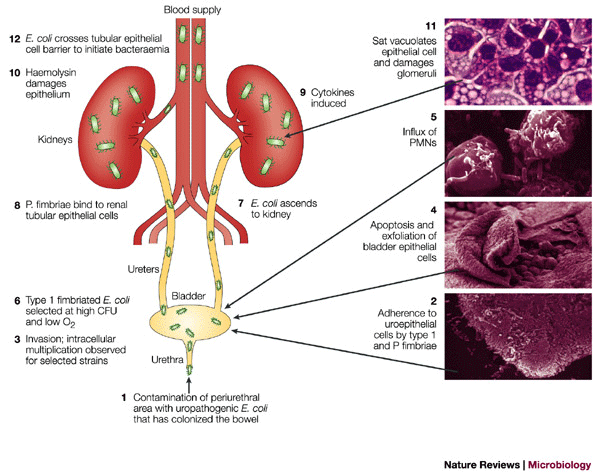
The figure shows the different stages of a Urinary Tract Infection.Overview Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection involving the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. These are the structures that urine passes through before being eliminated from the body.
Contents
1. Symptoms
2. Epidemiology
3. Diagnosis
4. Treatment
5. Prevention
6. Problems that can
caused UTI7. Types of UTI
8. Self-Care Tips
9. Medications
The kidneys are a pair of small organs that lie on either side of the spine at about waist level. They have several important functions in the body, including removing wastes and excess water from the blood and eliminating them as urine. The ureter, a narrow tube about 10 inches long, drains urine from each kidney into the bladder. The bladder is a small saclike organ that collects and stores urine. When the urine reaches a certain level in the bladder, the muscle lining the bladder contracts to expel the urine. The urethra is a small tube connecting the bladder with the outside of the body. A muscle called the urinary sphincter, located at the junction of the bladder and the urethra, must relax at the same time the bladder contracts to expel urine. Any part of this system can become infected. As a rule, the farther up in the urinary tract the infection is located, the more serious it is. The upper urinary tract is composed of the kidneys and ureters. Infection in the upper urinary tract generally affects the kidneys (pyelonephritis). The lower urinary tract consists of the bladder and the urethra. Infection in the lower urinary tract can affect the urethra (urethritis) or the bladder (cystitis).